Crabs scuttle among mangrove roots in a dense riverbank forest in southern Senegal, where a major reforestation project is reviving wildlife and boosting the west African country’s lukewarm economy.
“Everything you see here has been replanted. Before 2006, there wasn’t a single tree,” said Senegalese environmental activist and government minister Haidar El Ali in Tobor, a village near Ziguinchor, the main city of the Casamance region.
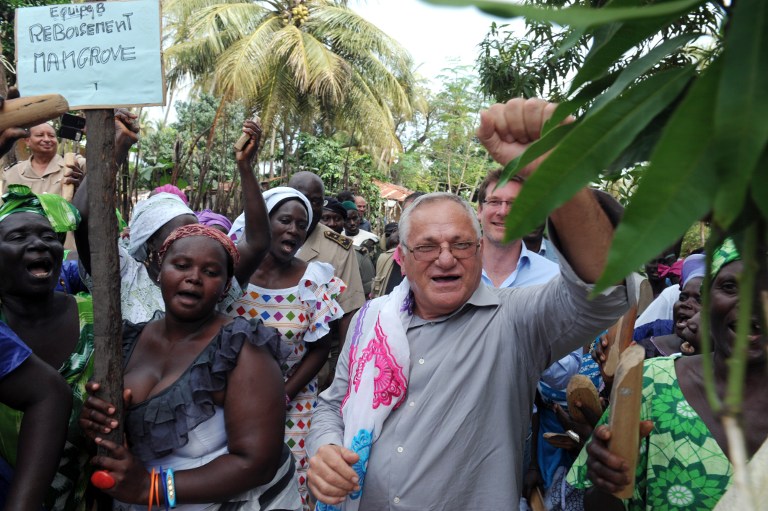
He gestured toward mangroves tied to stilts bordering the Casamance river, planted by his Oceanium environmental organisation to boost an area that experts said was severely depleted by deforestation, drought and increased salt levels in the water.
Alongside the road leading to the neighbouring Marsassoum valley, and around the paddy fields used in the centuries-old activity of rice cultivation, various mangrove species are abundant.
The habitat was destroyed through decades of illegal logging in mangrove forests for firewood and building.
“There has been nothing here since the 1960s and 70s. Replanting is bringing back the mangrove,” said Simeon Diatta, the chief of Diakene Diole village near the Guinea-Bissau border, pointing at riverside vegetation.
Reforestation revives mangroves
Since 2006, reforestation has revived 12 000 hectares (30 000 acres) of mangrove in Senegal – an area larger than the city of Paris – mainly in Casamance but also in the north and centre of the country, according to official figures.
“I am struck by the extraordinary success that this initiative represents,” French Development Minister Pascal Canfin said on a recent visit to Casamance, descriving the programme as “model for Senegal, Africa and the world”.
“With the return of the mangrove, people are catching a lot of fish and oysters. Women are selling them on and making a lot of money,” Diakene Diola resident Simeon Diatta told AFP.
The mangrove, which thrives in salt water, is important for trade in forestry and fishery products.
The swamps provide a nursery area for many marine species, most of which are important for food such as fish, crabs and shrimp.
In the nearby village of Diakene Ouolof, resident Mariama Tine said “everything was dead” before the replanting programme began.
“The mangroves stopped the advance of salt and we were able to recover rice fields. There were no fish here before but we are starting to get a lot of them, along with oysters and ark clams,” she said.
Mangroves vital to indigenous worship
Tobor mangrove farmer Mamadou Faye Badji says the ecosystem created by the tree is also vital in the worship rituals of the region’s indigenous people.
“The totems of the Diola are all in the forest. If forests are not dense enough, they will not stay here,” he told AFP, while Fisheries Minister Haidar El Ali said the mangrove had become part of the cultural heritage of the region’s villagers.
The damage done to mangrove swamps by deforestation remains “enormous”, however, and the battle is far from won, according to an environment ministry official.
Senegal’s economy is concentrated on fishing, tourism and groundnut production, with limited mineral resources and a narrow export base.
While the country has a long history of stability, its growth is below average on the continent and the reforestation is expected to contribute to an improvement.
Yet the project is not without controversy, with some believing the mangrove tree’s abundance is detrimental to the production of rice, since paddy areas are increasingly making way for mangrove swamps.
Lecturer Pape Cherif Bertrand Bassene mused in a recent column for the Quotidien daily newspaper that locals in Casamance, rather than welcoming the reforestation workers, should be decrying their “ignorance of tradition which results in a policy that does violence to this rice-growing culture”.
Bassene said reforestation had led to the “unavoidable consequence of divorcing the Casamance youth from their traditional rice-growing roots” and had reestablished mangrove swamps that local people “have always cut down to turn them into rice fields”.
Malick Rokhy Ba for AFP