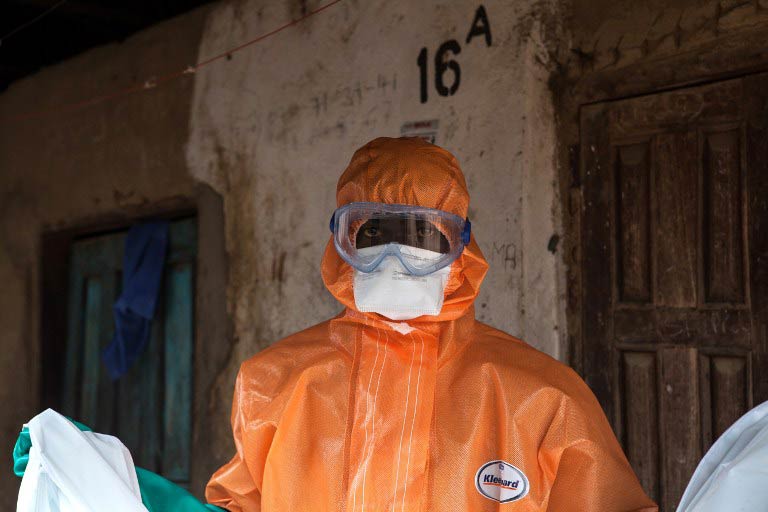
Watching with horror as the Ebola crisis ravages their country, Sierra Leoneans in London are mobilising to help their compatriots fight the deadly virus back home.
Health workers are taking leave from their jobs in the state-run National Health Service (NHS) to volunteer in Sierra Leone, where at least 1 200 people have died so far.
Others are raising funds for medical supplies, protective clothing and even hot meals for those affected – anything that makes a difference.
“I see it as a call of duty – I need to go down and help my people,” said Ajan Fofanah, a 46-year-old trained paediatric nurse who has applied to spend eight weeks working in Sierra Leone.
He was born in the west African country and moved to Britain aged 27 to further his education. Now he wants to use his skills to help battle the virus that has killed four members of his extended family.
“I’m far away from them and this is what is heart-rending. I need to get closer,” he added.
Fofanah was one of around 80 Sierra Leonean medics who attended an event in London last week to find out more about how they could help.
All were successful professionals keen to put their careers in Britain on hold and even risk being infected with Ebola to help their country.
Mohamed Koker, a 50-year-old emergency doctor who has worked in Britain for 12 years, hoped his knowledge of languages and traditions would help break down barriers with locals.
“I think the urge within me to perform what I call a national duty overrides my fear,” he told AFP.
“Most importantly, I have all the Sierra Leoneans back home who have no medical knowledge and who are sacrificing themselves, who are doing more than I think I am doing here.”
It is not only doctors and nurses who are desperate to help.
The British government is leading the international aid effort in its former colony, but members of the 23 000-strong Sierra Leonean diaspora here want to go further.
Ebola “is the only topic of conversation” among many, said Ade Daramy, chairman of the Sierra Leone Diaspora Ebola Task Force, which is working to help co-ordinate the response.
Food campaign, clothing
“When you live overseas and you’ve got family there – that just breaks you,” added Memuna Janneh, a 46-year-old British business consultant who grew up in Sierra Leone.
She started a charity in London to help feed people working on the frontline in Freetown, helped by her husband and relatives who are still living over there.
“LunchBoxGift” provided 2 600 meals to people living rough during the three-day lockdown in September, and now hopes to provide 50 000 more to hospital workers and patients.
“We may not have the cure, we may not have the logistics, we may not have the hospitals, all of those more complicated things that the government is battling to deal with,” she told AFP.
“But we can certainly as ordinary people come together to do food. It was really that simple for me.”
The British-based Sierra Leone War Trust for Children (SLWT) has also raised money to provide protective clothing and non-contact infrared thermometers for health workers and to deliver handwashing stations to rural areas.
In another innovative project, it sent 1 000 plastic raincoats to provide basic protection from Ebola for drivers of the “okada” motorcycles commonly used for transport.
For some, the urge to help is fuelled by a desire to save Sierra Leone from another trauma as serious as the country’s 1990s civil war.
Mayene Sesay (32) saw her mother shot dead in 1999 and lost a foot when a house she was in was set on fire.
She now runs an NGO for young disabled people in Sierra Leone.
Although not a medic, she attended the recruitment event in London to find out what she could do to fight Ebola.
“Whatever happens to me, I’m going to stay strong and help my country because I don’t want (it) to go through something else again,” she said.
“At least I can remember the person who shot my mum but I cannot see Ebola, where it comes from, how it affects my family. It’s like a ghost – you’re gone.”