On a recent Thursday at around midday, I saw a group of kids, not more than 15, who by their size appeared to be in nursery school.
The little boys and girls in pink checked shirts and grey pair of shorts were clustered in front of televisions on display.
They were pointing at a monkey swinging on the screens. They sighed in awe when they saw the close-up shots of ants. Around them were aisles after aisles full of new products for sale.
When I saw them, I thought: “Wow, these kids are out shopping at this hour … shouldn’t they be in class?”
However, unknown to me they were in class. Their teacher had brought her class on a trip to a SUPERMARKET.
Let that sink in.
A supermarket.
That one place that we dash into quickly to get a few things was their location for an educational trip.
Their teacher enthusiastically showed them why the many TVs in different sizes were on the shelves and why they had price tags on them. And that was not all; she was also describing to these young children why certain aisles were labelled the way they were.
Soap.
Body lotion.
Glass.
Again, a trip to a supermarket.
It stood out for me because school excursions during my primary school days were always out of town, probably to a beach or an agricultural institution or to the zoo or the airport – what I would now consider ‘educational’. A supermarket, in my view, was the least educational place for any learner.
But I was wrong.
From the looks of things and by the teacher’s thorough explanation of what happened here, you could tell this was an important trip.
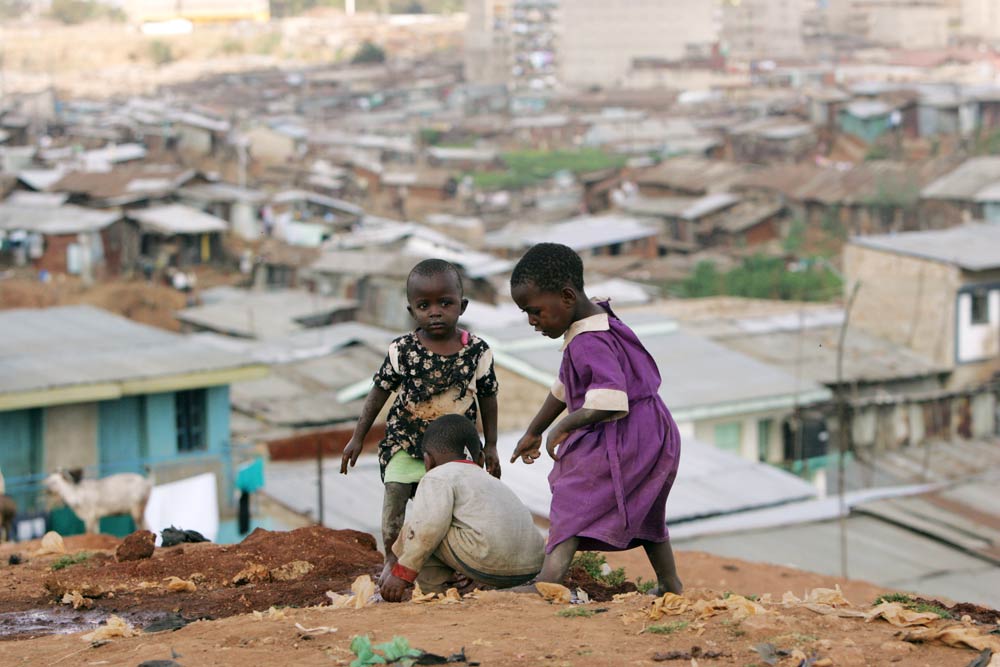
The supermarket is in Mathare North. Mathare in Kenya is an area known for slums (second to Kibera), violence and more slums. In fact a quick search on Google shows you that the extent of poverty here is on another level.
Indeed it is true. I know, I live here.
The area has informal settlements popping up all over. Every few hundred metres you are bound to find a burst sewer that flows into water pipes, and food vendors. You will see clinics and health centres competing for space with bars and entertainment joints. You will see stalls lined up, trying to attract potential customers with their music, sales pitches or adverts.
There are car washes, colourful matatus (public taxis) and happy children playing on the road side. There are high-rise houses so close to each other that if one tenant has a cold, the neighbour next door would probably pick it up. That close. There are electricity wires in meshes swaying and scrapping the air in the Mathare skies.
Each day as I get into a matatu to town, I pass school children who, despite their torn socks and faded uniforms, carry paper bags full of books as they head to class. I see little boys and girls bracing the morning chill to get to school.
It was only when l I bumped into the class on this trip that I realised their lessons were both in and out of the classrooms.
I deduced that their teacher wanted to show them the available possibilities amidst the sea of poverty they knew. There was such a high level of want that these young minds would look forward to attending class the next day, pegged on the possibility of stepping into a supermarket that they either passed by every morning or whose branded paper bags they saw on the streets.
Seeing these inquisitive children asking why the soaps were put away from the bread and maize flour made me realise that while this visit to the supermarket was ordinary to me, it was probably a first for these little leaders.
You could see the admiration in their eyes as shoppers carried items passed them. It hit me that this trip was the opening of new chapters in these children’s lives. That beyond the mire of life in a slum town as they know it, there was so much more available. So much variety was presented to these kids but circumstances had hindered them from reaching out to them.
I saw this and I was challenged to take a fresher look at the things I have and assume exist for everyone else.
Later, the children filed past the teller and each was given a lollipop on their way out. Some of them began to undo the lollipop wrappers in glee. Then I noticed one who looked at his sweet for a while and then simply put it into his shirt pocket, stretched out his palm and joined his hand to complete a chain of little hands and glossy excited eyes.
Once their lesson for the day was over, they streamed out with their teacher.
Eunice Kilonzo is a print journalist and storyteller who tells tales on development, feminism and health. Connect with her on Twitter: @Eunicekkilonzo