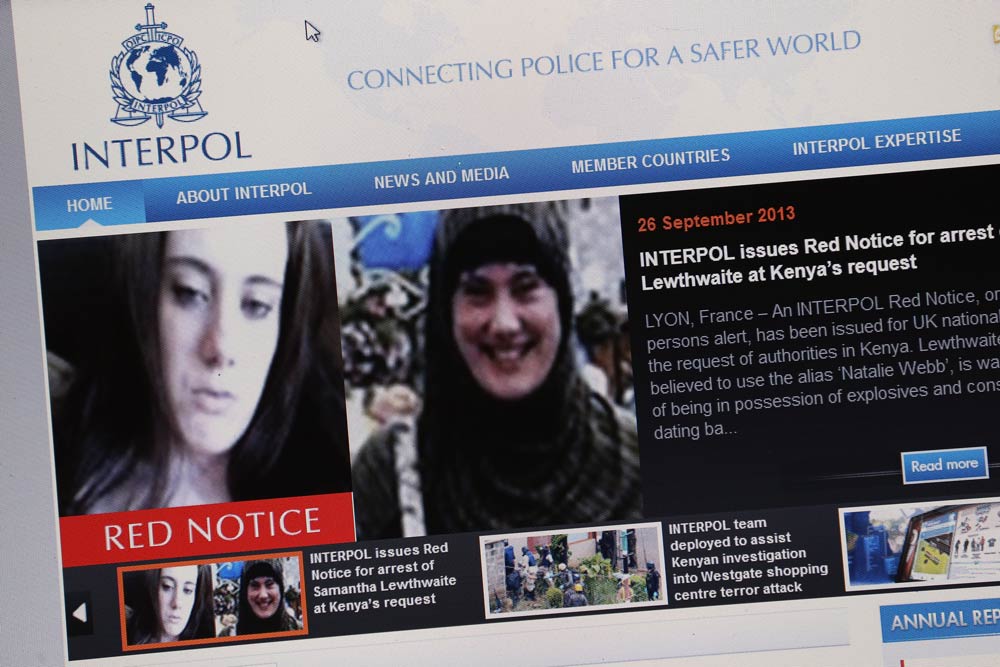
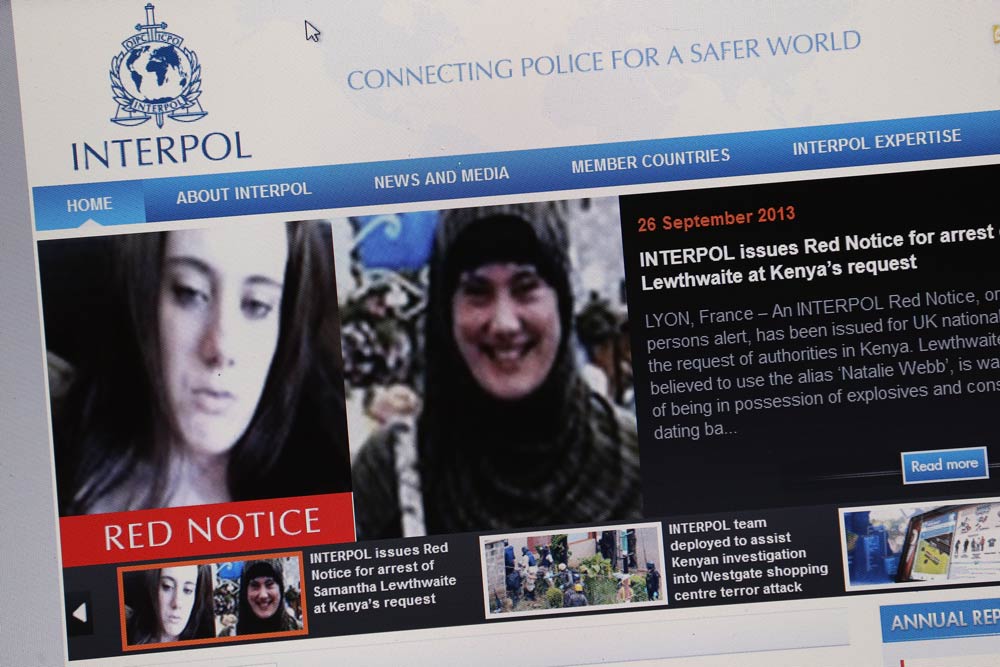
From a Kenyan perspective, the last decade has pretty much been a wasted opportunity for the country’s relationship with the United States. The election of Barack Obama had raised hopes of a deeper and more meaningful engagement given his Kenyan roots. However, it coincided with two seminal events of Kenyan presidential ballot history. This was the violence that followed the disputed vote in 2008 and, five years later, the election of a crimes against humanity indictee to the highest office in the land.
Like Mwai Kibaki before him, President Uhuru Kenyatta came to office with a serious legitimacy deficit. His administration too is hobbled by corruption and has been accused of clamping down on civic freedoms. Coupled with Obama’s own troubles at home, as a loony fringe loudly questioned whether he was sufficiently American, these, inevitably created a regrettable distance between the two countries. The situation was perhaps best summed up in then Assistant Secretary of State Johnnie Carson’s statement on the eve of the 2013 election: “choices have consequences”.
The UK also issued similar warnings of minimal contacts should Kenyatta and his running mate, William Ruto, both of whom had been indicted by the International Criminal Court over the 2008 post-election violence, win the polls. Though these eventually turned out to be hollow, the perceptions of Western interference supercharged the duo’s campaign and helped get them elected.
Once in office, as part of their push to get their cases dropped, UhuRuto (as they became known) fanned anti-Western sentiment both at home and across the continent, painting the ICC, in the words of Uhuru’s address to the African Union, as a “toy of declining imperial powers”, and playing up the new engagement with China as a counterweight to the West.
Obama too was keen to keep his distance. Following the example of his immediate predecessors, he made a point of skipping Kenya on the two African tours of his first term. If anything, it appeared that Tanzania, which is getting rather used to US presidential visits having hosted Bill Clinton, George Bush and Obama, seemed to be the US’s new BFF in the region.
One would thus have imagined that relations with the US had settled into the back of the freezer for the foreseeable future. It was all so different from 2008 when Kenya had been the only country in the world to declare a public holiday in celebration of Obama’s election.
So what changed?
Terrorism for one. Kenya has been a target of attacks from the Somalia-based al-Shabab terror group ever since it invaded its neighbour in October 2011. But under the Uhuru administration, the numbers and severity of attacks have skyrocketed. The government’s incompetent response has generated the possibility of a spreading Islamist-inspired insurgency across Kenya’s north-eastern border regions. The threat to the largest economy in East and Central Africa and a bulwark for regional stability simply could not be ignored. Perhaps Obama is betting that by re-engaging with Uhuru, he can gently nudge him to take the necessary measures to confront it.
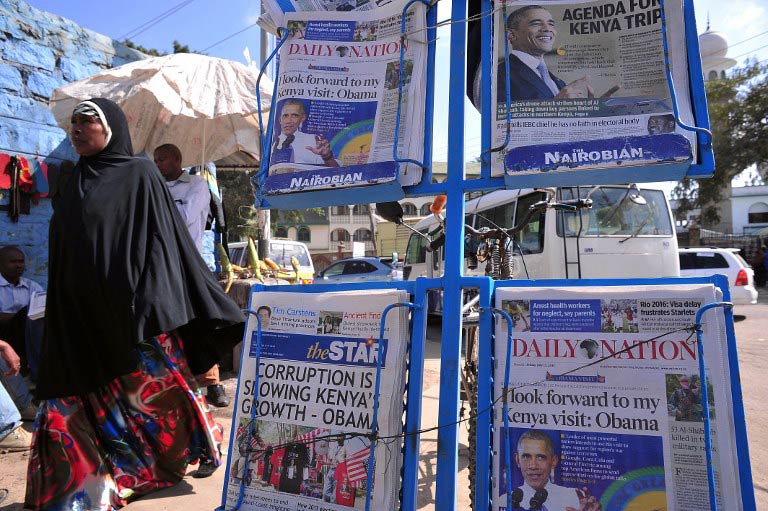
Secondly, it is important to note that the anti-Western rhetoric was always little more than a charade. The aim was to discredit the ICC, not alienate the West. It was not about taking Obama on, but getting Uhuru off. Under the surface, admiration for Obama ran deep. The two modelled their campaign and atmospherics on him, and across the country, as reflected in a 2014 Pew survey, Obama remains popular.
What are we to expect of the visit?
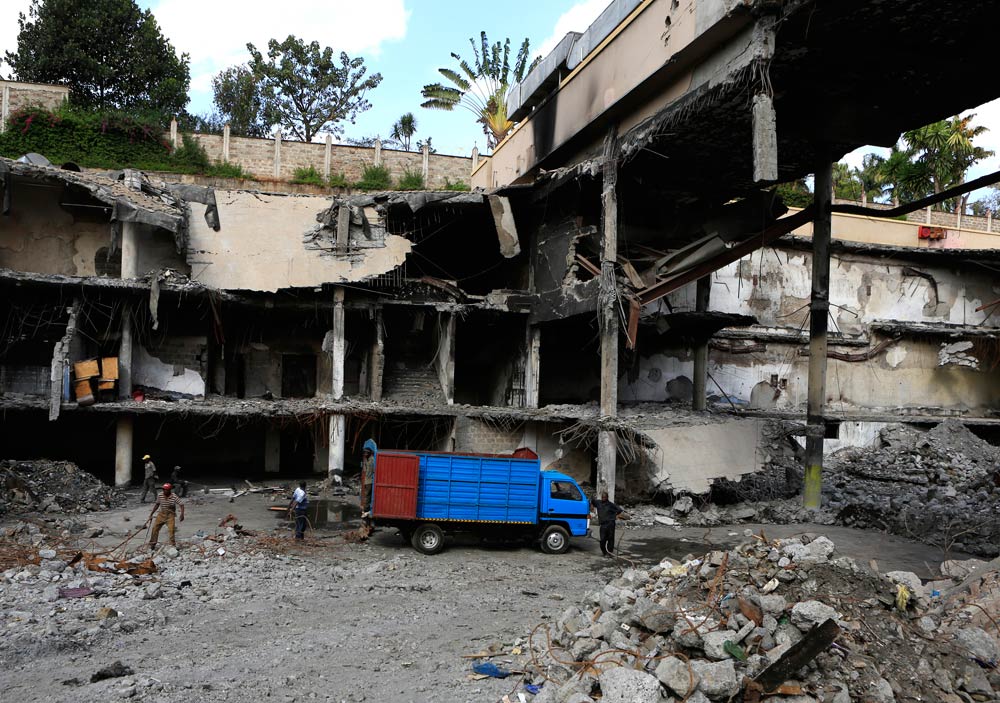
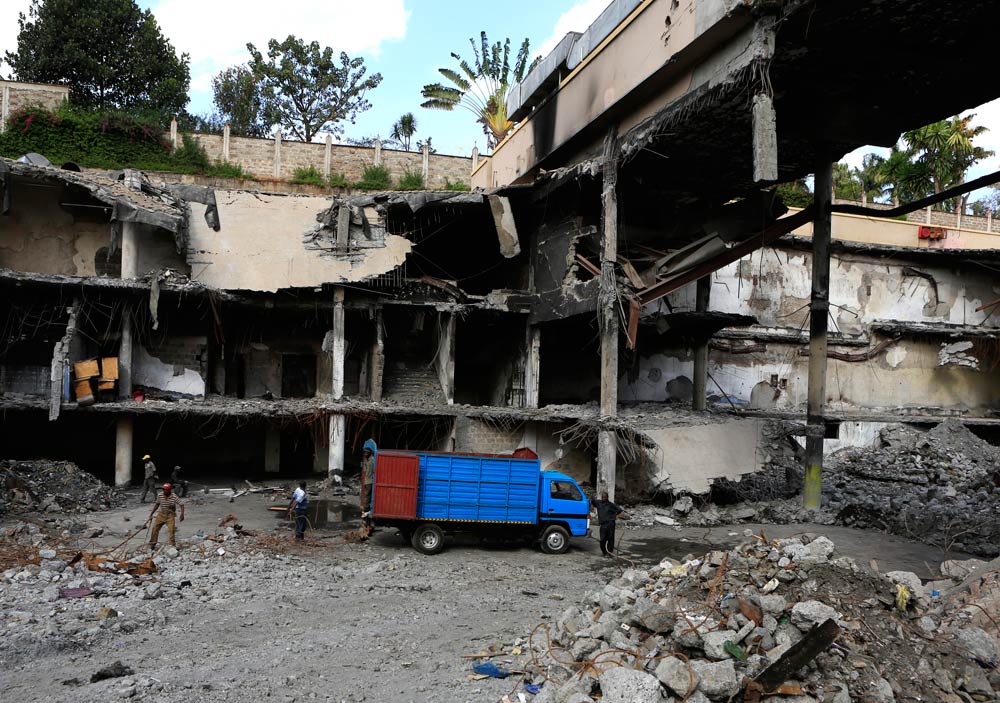
While the official reason Obama is coming is the Global Entrepreneurship Summit, there is little doubt that behind the scenes, it will be dominated by concerns over the worsening security and governance situation. Less than a week before Obama’s arrival, the reopening of the Westgate mall, scene of an al-Shabab massacre of at least 67 people two years ago, will be presented as a sign of resilience in the face of terrorism. But it also stands as a monument to the refusal by the authorities to learn lessons from previous attacks and to make much-needed improvements. Obama himself has said that counter-terrorism will be an important focus of the visit. And while he will probably be more restrained when criticising his hosts in public than he was during his visit as Senator in 2006, one would still expect some tough talking away from the cameras.
The Kenyan government will also probably be on its best behaviour. It is best to ignore the loopy-headed warnings of Obama being thrown out of Parliament if he mentions gay marriage – he is not even scheduled to address MPs. Ditto the mooted 5000-strong nude march to protest the issue.
Nairobi is being spruced up in anticipation of the visit but that will be cold comfort for its long suffering residents. The homeless are being rounded up and will be kept out of sight and with much of the city expected to be in virtual lockdown, the usually terrible traffic will be nightmarish. In fact there is talk of an “Obamigration” as those who can flee the city in advance of Obama’s arrival.
The visit will also be a boon to the country’s cops. A new directive of dubious legality requires that everyone in Nairobi carry ID or risk arrest. There is no law in Kenya that requires the carrying of documents on pain of detention and this will only create an avenue for rich pickings for 15000 members of the famously corrupt National Police Service as citizens try to avoid the prospect of a weekend behind bars.
The real test of the visit will be what happens after he leaves. Will there be any lasting change? It will be particularly interesting to see whether Obama is able to persuade Kenyatta to take security seriously and to stop using it as an excuse to clamp down on civil rights. Movement on that front alone would make all the hassle worthwhile.
Patrick Gathara is a strategic communications consultant, writer, and award-winning political cartoonist. To read more of Patrick’s opinion pieces visit his blog, Gathara’s World or follow him on Twitter: @gathara