With Zimbabwe’s economy on its knees and life a daily struggle for most people, there is one luxury that many can surprisingly still afford — laughter.
“We laugh at ourselves. We laugh at funerals. We laugh even when things are not going well for us and we should be moaning and groaning,” says award-winning dramatist and poet Chirikure Chirikure.
Out of difficult times, with unemployment rampant and poverty widespread, a new generation of comedians has emerged to give the stressed nation’s funny-bone a much-needed tickle.
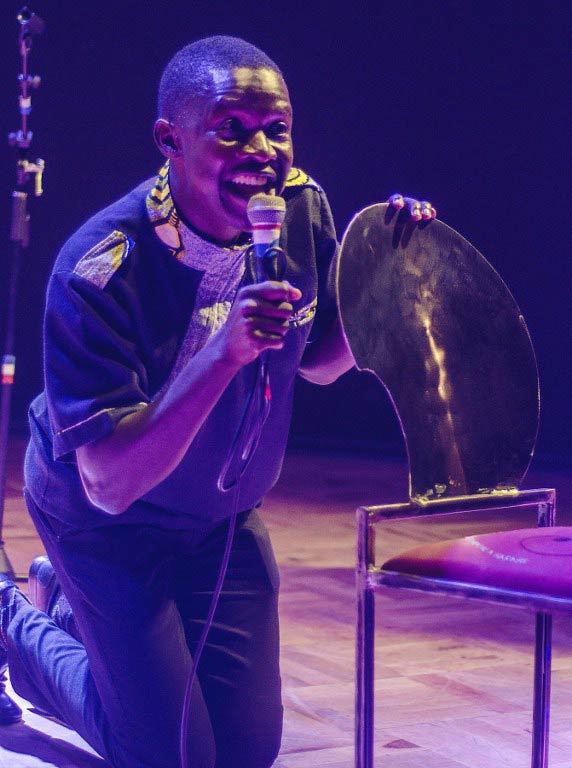
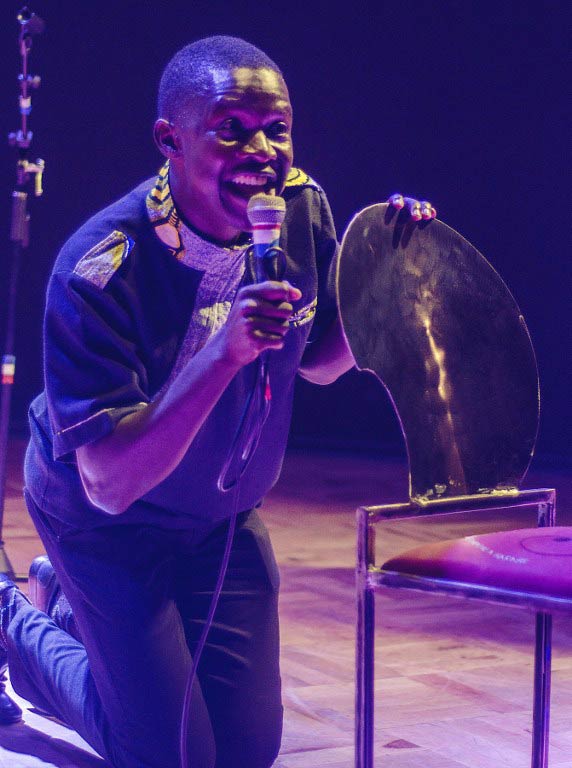
Simuka Comedy – made up of Victor Mpofu, better known by his stage name Doc Vikela or simply The Doctor, Michael Kudakwashe, Samm Monro and Comic King – attract full houses to their regular shows at The Book Café, a popular arts joint in the capital Harare.
The young comics spare no sacred cows as they poke fun at anyone from veteran President Robert Mugabe and his wife Grace to corrupt traffic police officers, former white commercial farmers and local celebrities.
Donning a doctor’s white coat and stethoscope, Mpofu dishes out what he calls “doses” of humour to audiences sick of hard times after 15 years of economic decline blamed on the policies of Mugabe’s government.
The “Doctor” has his audience in tears of laughter as he imitates the 91-year-old president announcing the list of countries he has just visited on one of his frequent trips abroad – while the government can’t find the money to pay civil servants’ salaries.
He also takes a dig at Mugabe’s 35 years in office.
“Zimbabweans, for all our literacy – with a 99.9995 percent literacy rate – we are the only country that will fail to answer a simple question: who is your former president?”
For many, Mugabe, who has been in power since independence in 1980, is the only leader they have known.
Explaining the growing popularity of their shows, Mpofu said relentless hard times made people look for comic relief.
“Humour is a medically proven stress reliever,” he told AFP.
“Things are tight and people need something to take the stress off their lives. People would rather spend their little cash laughing and drinking.”
Comedy fan and regular showgoer Enright Tsambo agreed, while noting that the drinking part of a night out was seriously limited by a lack of cash.
“We can’t afford to drink as much as possible so some of us just buy one beer and spend an evening laughing at a comedy show,” he said. “It takes the stress away.”
In a country where insulting the president is a crime punishable by up to a year in prison, the comedians have found a way of tackling serious issues without making direct statements, so they get away with jokes that could get ordinary citizens arrested.
Fun and trouble
Away from the comedy venues, Zimbabweans share jokes across social media such as Facebook and WhatsApp and through street theatre shows – and some of them have landed in trouble.
“We have had several cases where people have been prosecuted for freely expressing themselves and in most cases they will just be sharing or cracking a joke,” said Kumbirai Mafunda, spokesman for Zimbabwe Lawyers for Human Rights.
He cited the examples of a woman facing charges of insulting Mugabe after she sent a picture on WhatsApp purportedly showing the president in the nude, and a man who was arrested for joking that Mugabe was so old he would have a hard-time blowing up his birthday balloons during national celebrations earlier this year.
Mpofu’s colleague Samm Monro, better known by his stage name Comrade Fatso, pokes fun at the internal feuding which has seen factions in Mugabe’s Zanu-PF party waging bitter fights among themselves in the race to succeed him.
“Zanu-PF is the biggest opposition to Zanu-PF and now what is (opposition leader) Morgan Tsvangirai supposed to do?” Monro queried in one of his sold-out acts at the recent Harare International Arts Festival.
The University of Zimbabwe also came in for ribbing as the record holder for the fastest conferment of a doctorate – after Mugabe’s wife Grace was awarded a PhD three months after registering.
Monro is also among newscasters on the satirical Zambezi News, which parodies the state broadcaster Zimbabwe Broadcasting Corporation, renowned for its pro-government spin.
Zambezi News bulletins, shown online on YouTube and on stage, feature characters such as the Minister of Impending Projects and the Minister of Mines, who owns a mine called Mine Mine – “because it’s mine”.
In the news bulletins white farmers whose properties were expropriated during the country’s controversial land reforms – partly blamed for the country’s economic collapse – are called “formers or farmers because most of them are former farmers”.
One of the country’s top production houses has produced a play, All Systems Out of Order, portraying the collapse of amenities such as public toilets as a symbol of the state of the country.
“There is so much pain, and people find solace in looking at themselves and laughing at themselves,” said theatre producer and actor Obrien Mudyiwenyama.