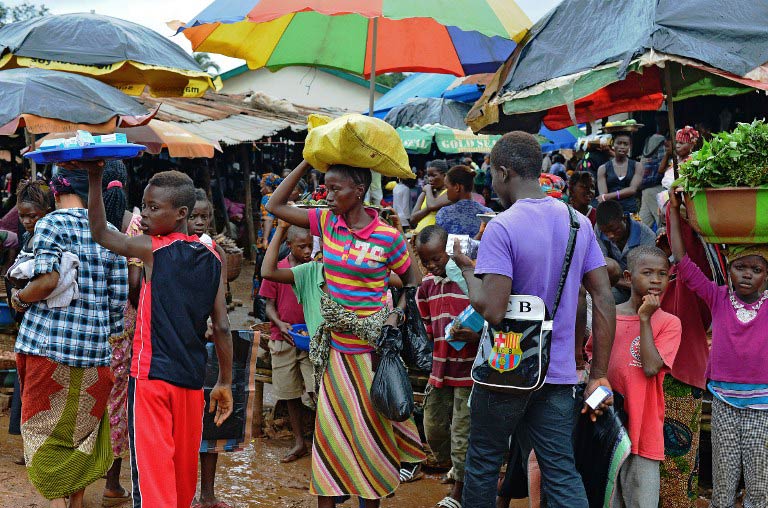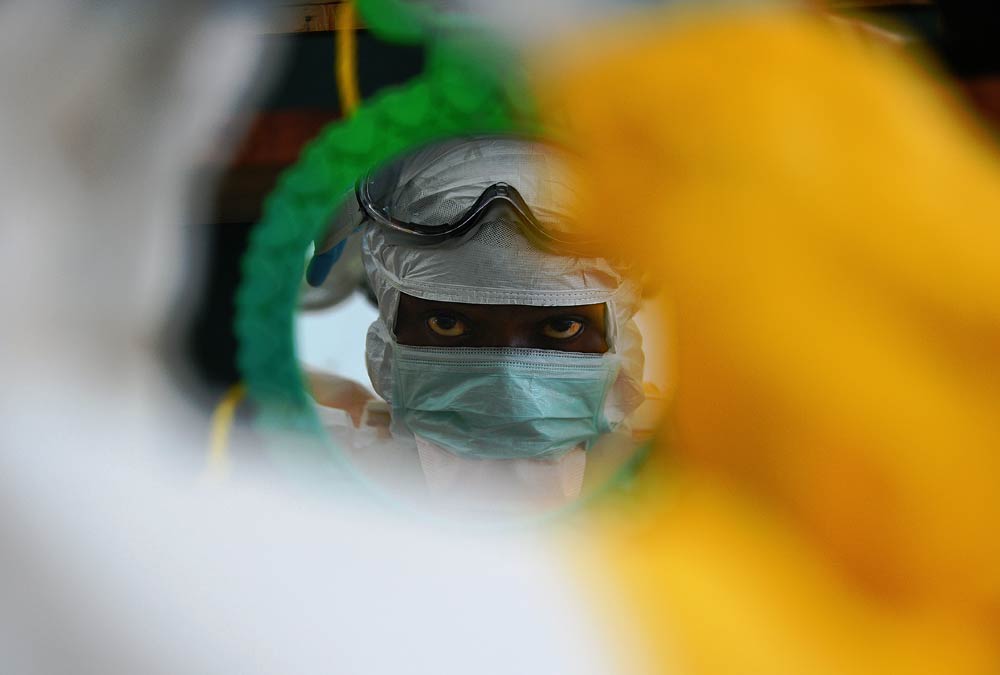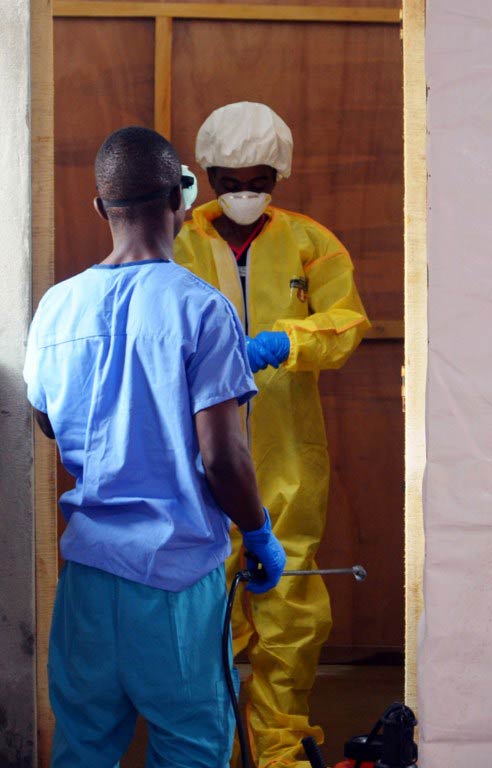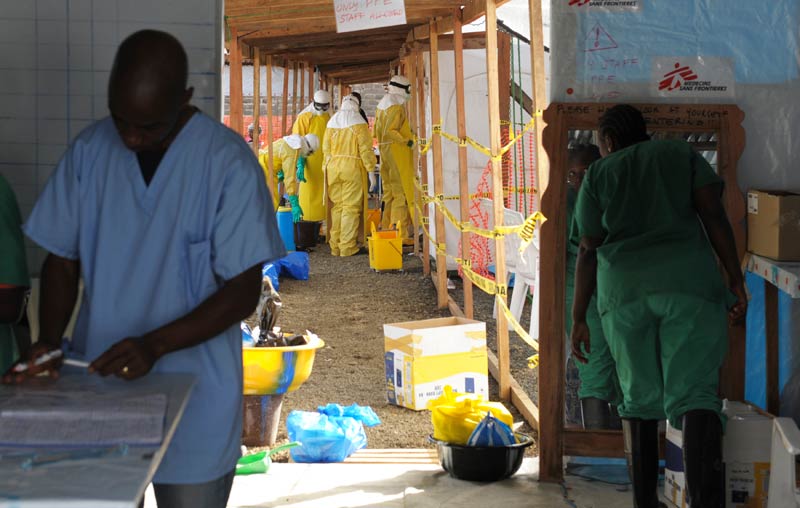
Ebola is threatening the very existence of Liberia as the killer virus spreads like “wild fire”, the defence minister warned Tuesday, following a grim World Health Organisation assessment that the worst is yet to come.
After predicting an “exponential increase” in infections across West Africa, the WHO warned that Liberia, which has accounted for half of all fatalities, could initially only hope to slow the contagion, not stop it.
“Liberia is facing a serious threat to its national existence,” Defence Minister Brownie Samukai told a meeting of the UN Security Council on Tuesday.
The disease is “now spreading like wild fire, devouring everything in its path,” he said.
The WHO upped the Ebola death toll on Tuesday to 2 296 out of 4 293 cases in Liberia, Sierra Leone, Guinea and Nigeria as of September 6. Nearly half of all infections had occurred in the past 21 days, it said.
The agency also evacuated its second infected medical expert, a doctor who had been working at an Ebola treatment centre in Sierra Leone.
Emory University Hospital in the United States admitted an American on Tuesday who had contracted the disease in west Africa, but declined to confirm whether the patient was the WHO employee.
The hospital has successfully treated two other infected US nationals.
Ebola, transmitted through bodily fluids, leads to haemorrhagic fever and – in over half of cases – death. There is no specific treatment regime and no licensed vaccine.
The latest WHO figures underscore Ebola’s asymmetric spread, as it rips through densely populated communities with decrepit health facilities and poor public awareness campaigns.
Speaking on Tuesday, WHO’s epidemiology chief Sylvie Briand said the goal in Senegal and Nigeria was now “to stop transmission completely”. Senegal has announced only one infection, while Nigeria has recorded 19 infections and eight deaths.
The Democratic Republic of Congo is battling a separate outbreak which has killed 32 in a remote northwestern region.
“But in other locations, like Monrovia, where we have really wide community transmission, we are aiming at two-step strategies,” Briand said in Geneva, “first, to reduce the transmission as much as possible and, when it becomes controllable, we will also try to stop it completely.
“But at this point in time we need to be pragmatic and try to reduce it in the initial steps.”
A day earlier the WHO had warned that aid organisations trying to help Liberia to respond would “need to prepare to scale up their current efforts by three- to four-fold”.
Before the current outbreak, it noted, Liberia only had one doctor for every 100 000 patients in a population of 4.4 million.
In Montserrado county, which contains Monrovia, there are no spare beds at the few Ebola treatment sites operating, the WHO said.
It described how infected people were being driven to centres only to be turned away, return home and create “flare-ups” of deadly fever in their villages.
It said 1 000 beds are needed – far more than the 240 currently operational and 260 planned.
Guinea’s President Alpha Conde described Ebola as a “war” his nation – with 555 dead so far – needed to win.
He slammed neighbouring states including Côte d’Ivoire and Senegal for shutting their borders, and airlines for suspending flights to affected countries.
“They forget that when you close borders, people just go through the bush. It’s better to have official passages of transit,” he said.
African Union commission chief Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma also called Monday for travel bans to be lifted “to open up economic activities”.
In Gambia, customs officials said Tuesday they had closed the borders to Guineans, Liberians, Nigerians and Sierra Leoneans – though not to neighbouring Senegal.
“We are also advising Gambians intending to travel to these countries to cancel their trips, but any Gambian who fails to heed our advice, we will not allow you in the country if you return,” Ebrima Kurumah, a health officer posted at the border with Senegal, told AFP.
There were restrictions further afield, too. China, one of the region’s main investors, announced on Tuesday it was reinforcing checks on people, goods and vehicles – and even mail – arriving from affected countries.
Meanwhile, Italy announced its first possible case of Ebola – a woman recently returned from Nigeria.