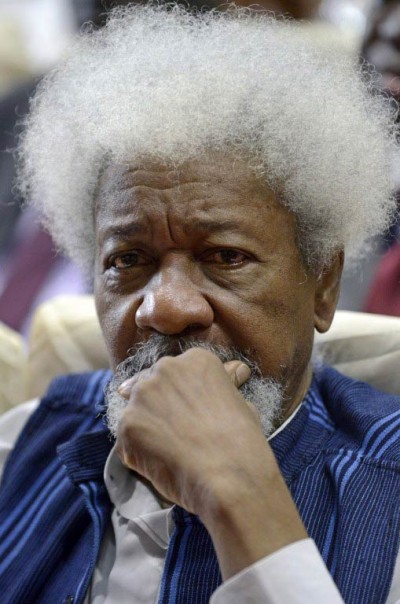
Nigeria’s literary icon Wole Soyinka turned 80 on Sunday, with friends and foes alike paying tribute to the first African to win the Nobel literature prize.
Dozens of literary and artistic events have been staged across the country over 80 days leading up to the birthday of the poet, novelist, playwright and social activist, whose works often satirised Nigeria’s society and harshly criticised corrupt and inept leaders.
But such is Soyinka’s popularity and stature that many of the targets of his criticism put aside past differences to honour the man who, with his trademark white afro and matching bushy goatee, is a beloved figure in Africa’s most populous nation.

President Goodluck Jonathan praised his ardent critic in a statement on Saturday, hailing Soyinka’s “life-long dedication and indefatigable commitment to using his acclaimed genius and talents, not only in the service of the arts, but also for the promotion of democracy, good governance and respect for human rights in Nigeria, Africa and beyond”.
Former dictator General Yakubu Gowon, who jailed Soyinka for some two years during Nigeria’s 1967-1970 civil war, paid respect by attending a lecture in Soyinka’s hometown of Abeokuta on Friday.
Soyinka, who looks several decades younger than his age, sprang to his feet and warmly embraced his former jailer as soon as he entered the lecture hall, sparking applause from the audience.
“I have come to Abeokuta for the sake of this particular man, to honour him,” said Gowon, who imprisoned the writer on suspicion of support for his rival in the 1967 standoff that eventually led Nigeria to a 30-month civil war in which an estimated one million people died, mostly of disease and starvation.
The birthday events honouring Soyinka are due to culminate on Monday with a visit to his secluded forest residence in Abeokuta, the capital of southwestern Ogun State, and a presentation of one of his plays.
Born into an Anglican family on July 13, 1934, in Abeokuta, Soyinka cut his literary teeth in the 1950s at the University of Ibadan, Nigeria’s premier university, where he studied English literature.
He also studied literature at the University of Leeds.
Darling of the critics
The poet, novelist and playwright has around 30 published works to his name, most of which satirise Nigerian society and which have made him a darling of the critics.
“Soyinka, a literary giant, is God’s gift to Nigeria in particular, Africa and the world at large. His style is inimitable,” Dare Ademola, a literary critic, told AFP.
Chima Anyadike, head of the English department at the Obafemi Awolowo University where Soyinka last taught in Nigeria, said: “Soyinka is a great writer of his time.”
In announcing his Nobel in 1986, the Swedish Academy praised Soyinka for “your versatile writings (in which) you have been able to synthesise a very rich heritage from your own country, ancient myths and old traditions, with literary legacies and traditions of European culture”.
It also hailed him for “your own genuine and impressive creativity as an artist, a master of language, and your commitment as a dramatist and writer of poetry and prose to problems of general and deep significance for man, modern or ancient”.
A harsh critic of military, corrupt or inept governments, Soyinka fled Nigeria during the regime of General Sani Abacha in the 1990s when the government hounded critics including journalists and academics.
A hunter, connoisseur of wines and notoriously private, Soyinka hasn’t let his advanced age dull his social activism. In January 2012, he joined activists in street protests against President Jonathan after the government hiked the pump price of fuel.
Aderogba Obisesan for AFP