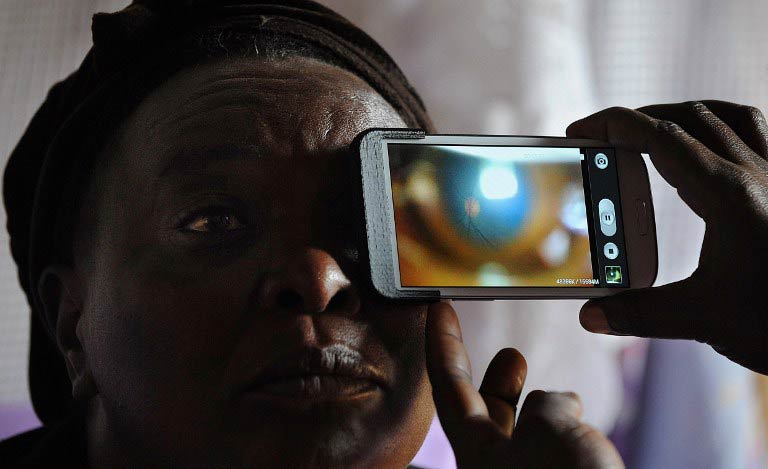
Simon Kamau (26) has been in almost constant pain since he was a playful three-year-old and accidentally pierced his eye with a sharp object, but smartphone technology now offers hope.
His family live in an impoverished part of rural Naivasha in Kenya’s Rift Valley region and could not afford the 80km journey to the nearest specialist hospital, leaving the young Kamau blind in one eye ever since.
Today, 23 years later, Kamau has a chance to better his quality of life thanks to a team of doctors from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine armed with an innovative, low cost, smartphone solution.
“Kenya was a natural test location,” the project’s team leader, Dr Andrew Bastawrous, told AFP. “For a country with a population of more than 40 million, there are only 86 qualified eye doctors, 43 of whom are operating in the capital Nairobi.”
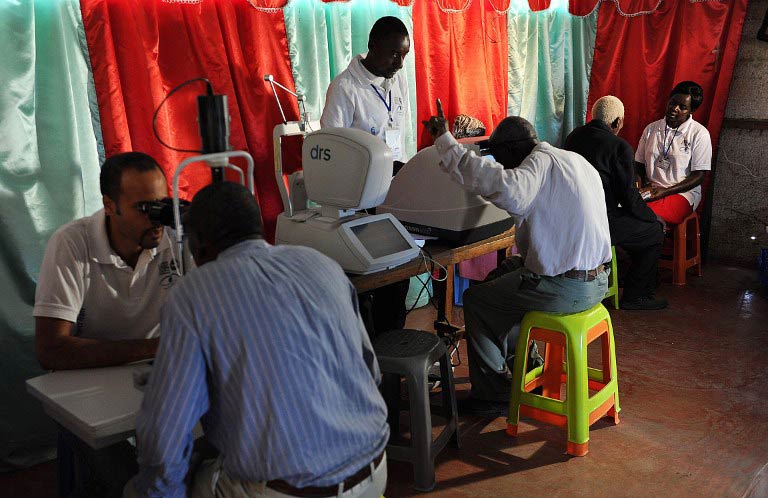
The equipment used in the study, which has been running for five years and is now in its final stages, is a smartphone with an add-on lens that scans the retina, plus an application to record the data.
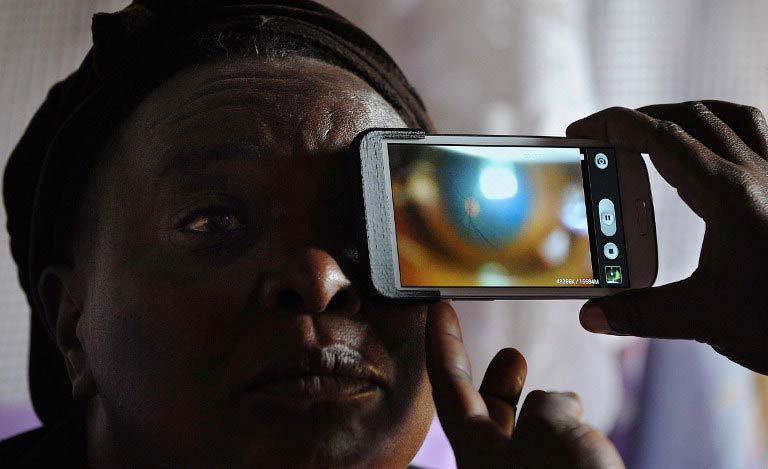

The technology is deceptively simple to use and relatively cheap: each ‘Eye-Phone’, as Bastawrous likes to call his invention, costs a few hundred euros, compared to a professional ophthalmoscope that costs tens of thousands of euros and weighs in at around 130kg.
Bastawrous said he hopes the ‘Nakuru Eye Disease Cohort Study’, which has done the rounds of 5 000 Kenyan patients, will one day revolutionise access to eye treatment for millions of low-income Africans who are suffering from eye disease and blindness.
With 80% of the cases of blindness considered curable or preventable, the potential impact is huge.
Data from each patient is uploaded to a team of specialists, who can come up with a diagnosis and advise on follow-up treatment. The results are also compared to tests taken with professional equipment to check the smartphone is a viable alternative.
Bastawrous says his ‘Eye-Phone’ has proved its worth, and can easily and accurately diagnose ailments including glaucoma, cataracts, myopia and long-sightedness.
Treatments range from prescription glasses and eye drops to complex surgery that is conducted once every two weeks at a hospital in Nakuru, the nearest big town. So far, up to 200 of the 5 000 people involved in the study have had surgery to correct various eye ailments.
Kamau is among those expecting to receive surgery on his blind eye. While doctors say he is unlikely to recover his full vision because the injury was so long ago, they can at least stop the pain and swelling caused by the additional strain on his functioning eye.
“I can hardly do manual work around the farm. Once the sun shines, my eyes water and I feel a lot of pain,” said Kamau, who lives on a small farm with six family members.
Neighbour Mary Wambui (50) has had eye problems for 36 years but gave up on finding treatment because existing medical care was far too expensive. Instead, she settled for home remedies like placing a cold wet cloth over her eyes when the pain became unbearable.
“I was treated at the Kijabe Mission hospital but the follow-up visits became too expensive. I had to pay bus fares and then queue in the waiting room for the whole day, and then go back home without seeing a doctor,” she recalled.
She said Bastawrous’ project, in which the tests were carried out at her home, was a welcome relief.
“I do not like the feel of hospitals. Their process is long, laborious and costly but with this phone, I got to know of my diagnosis with just a click,” she said.
Bastawrous says the success of the smartphone meant it could soon be replicated in other poor areas of Kenya. He said the arid Turkana area, one of Kenya’s poorest regions, was next on the list.
Irene Wairimu for AFP