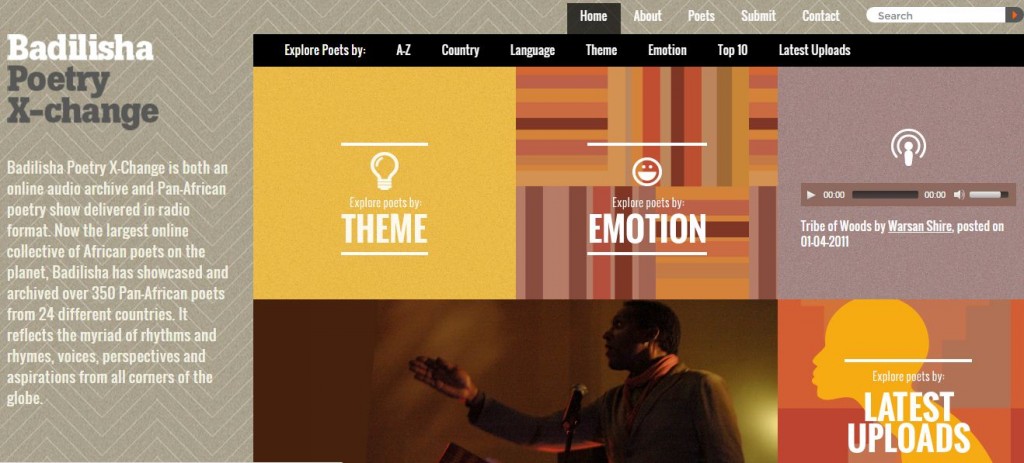
“I’ve lived two lives in this life.”
“How?”
“I had things, now I have nothing.”
“What are you afraid of most?”
“El Niño is coming.”
“And what makes you laugh?”
“Life.”
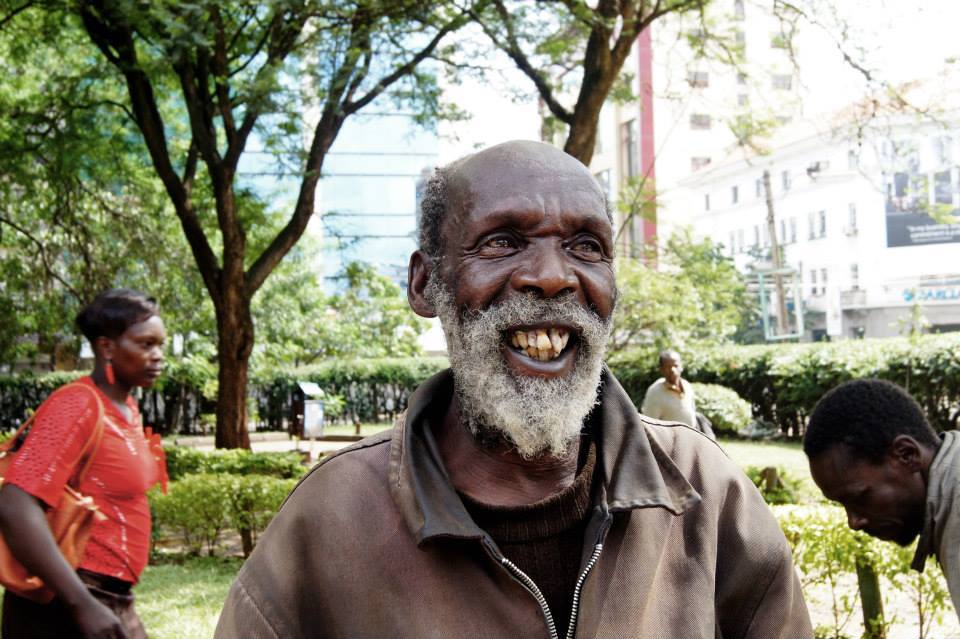
This was a conversation with Daniel, a destitute man in Nairobi, Kenya, posted on the internet last August. That night, thanks to a stranger, he received a cooked meal of ugali and stew. Then came more donations of food, money, clothes, a bed and a shack for him to live in.
Here lies the power of Homeless of Nairobi, a Facebook page pricking the conscience of those who take such things for granted.
It is “a virtual home” for the homeless people of the Kenyan capital and one of the few places where they are seen, heard and dignified.
The page features photos, conversations and updates on volunteer projects, such as a group effort on Christmas day that fed about 600 people with 600 loaves of bread, 500 packets of milk, 500 bananas and about 50 bottles of soda.
Not every story has a happy ending. “Today is a heartbreaking day for the Homeless Of Nairobi project,” read a post in November. “Over the past two months, we found a home for a wonderful man called Daniel… It has now come to our attention that Daniel has now left the house in favour of the streets once again. It is hard to understand why but we had told him that there is no pressure on him to stay.”
Building a movement
The page was launched last year by Sham Patel (29), who was born and raised in Nairobi but spent three years as a student in Liverpool in the UK. Like many other residents, he gave little thought to people without a home until a chance encounter gave him a flash of empathy and changed his perspective.
“Ever since I was young, I’ve seen homeless people on the streets of Nairobi,” he recalled this week. “They have become part of the wallpaper of this city. For a long time, I didn’t see them as people but as pests who bother people for money. We’re conditioned to think like that by an apathetic society from when we’re young. We’re pre-programmed.”
But then one rainy day, on his way to the gym, he saw some homeless people huddled under a plastic sheet. “It made me think about how I’d feel if that was me or my parents out in the rain without shelter and food. I decided then that it was time to try to make a small difference where possible so the next day I took them bread and milk and started a conversation with them and it was incredible how much they knew about life and their philosophies and belief in God was astounding.”
Patel added: “They shared the bread with me. In fact, they offered it to me first before they ate. Since then, I’ve decided to talk to and spread the stories of as many homeless people as possible with the hope that we can build a movement that will lead to finding ways to help these men, women and children that much of society and our government has discarded.”
One of his major inspirations for the format was Humans of New York, a popular website cataloguing photos, snippets and stories from the US city’s inhabitants. Patel met its founder briefly and was advised: “Just go for it.”
Since then he has gone out day and night, gathering dozens of photos and stories, and the page has gained more than 3 000 likes on Facebook. It offers a rare insight into the pitiless conditions of the homeless in a major African city who have little social support or sympathy from the police. Some turn to drugs for escapism from hunger, pain or misery. A poignant entry on Thursday with a picture of children read:
“How much is the bottle of glue you’re sniffing?”
“We get it for about 30 shillings.”
“So why don’t you buy a small meal with that 30 shillings?”
“Because that meal will not even be enough to fill my stomach. That food will not help me when it is cold at night or when I am hungry again. The glue lasts longer and helps me forget where I am.”
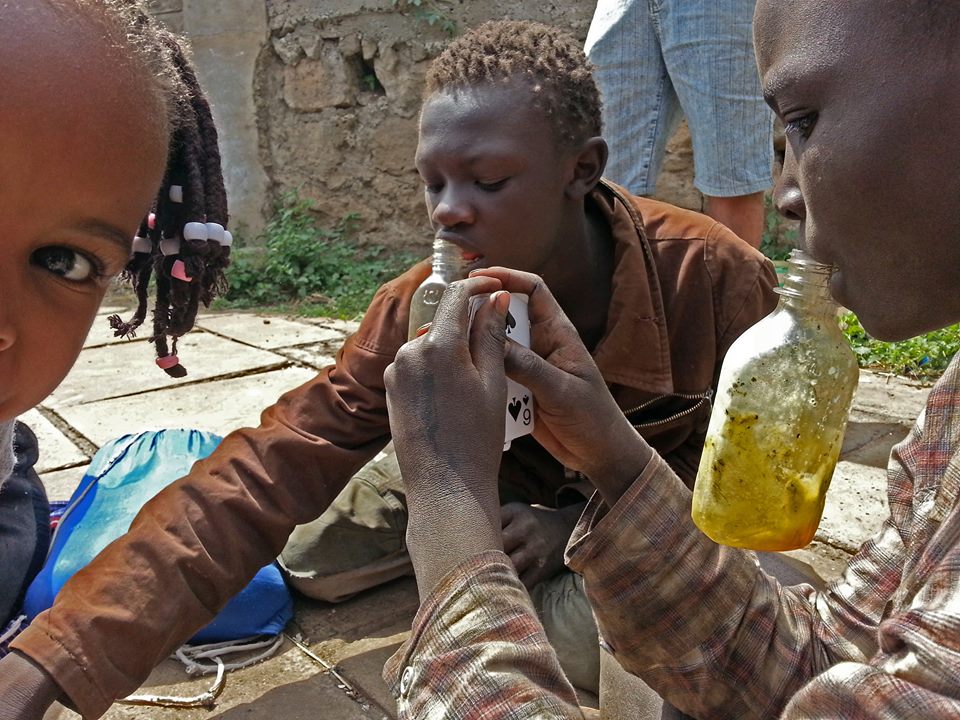

According to the charity Kenya Children of Hope, in 2007 it was estimated that there were 250 000 – 300 000 children living and working on the streets across the country with, with more than 60 000 of them in Nairobi.
Mixed responses
Patel said he gets a varied response from those he asks to take part. “Most of the time, the homeless people are really happy just to talk to someone and we can talk for a pretty long time. Other homeless people aren’t so friendly because of their lack of trust or because they’re high on something or the other.
“But it’s been pretty mixed. There was the time I was almost robbed by three homeless people and there was another time we were chased down the street by a homeless guy who, it turns out, is a little psychotic or just really angry. But for the better part, most homeless people are very accommodating even though they do not trust the colour of my skin.”
Patel, who also runs Myrobi, a company that deals in T-shirts and marketing materials with a business partner, says he hopes to achieve “big things” with the Homeless of Nairobi project, including crowd funded projects and a homeless shelter where people can learn skills such as pottery, farming, mechanics and stitching.
“We want to have a psychiatry unit at the shelter because a lot of these homeless people have seen and endured things that human beings should not see. For example, the homeless girls being raped in town constantly.
“These people need psychiatrists to help them deal with the problems they’ve faced. We don’t just want to create a place where we dump homeless people and feed them. We want to bring them back from the brink they stand on. And their resilience proves that it is possible to do exactly that.”
David Smith for the Guardian Africa Network