Since her university days, Kasha Jacqueline Nabagesera, an openly gay woman and activist in Uganda where homosexuality is illegal, has been a victim of vicious tabloid gossip.
“They were writing about ‘secrets inside the lesbian’s den’,” Nabagesera (34) told AFP. She said she had been attacked and evicted “so many times” because of the media coverage.
Now Uganda’s gay community is fighting back with Bombastic, a new magazine published and distributed privately.
The free 72-page glossy publication features personal essays, commentaries and poems by “proud” lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) Ugandans, some using pseudonyms.
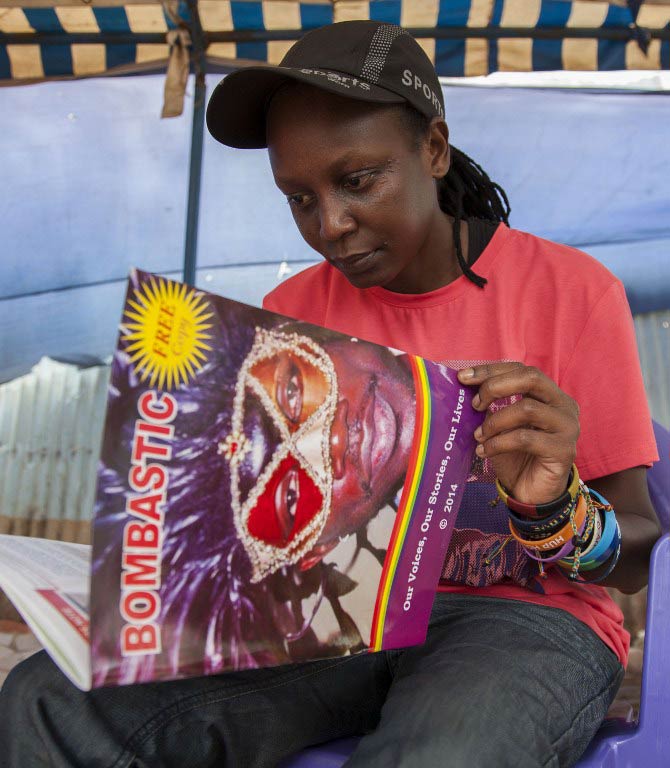

In the editor’s note Nabagesera said the magazine would “speak for the many voiceless”.
Uganda’s popular tabloid press has outed many of Nabagesera’s friends and colleagues, and regularly fills pages with invasive, prurient stories and lurid tales.
Politicians have stoked anti-gay sentiment by proposing new laws that appeal to the country’s conservative Christianity, the latest of which seeks to criminalise the “promotion” of homosexuality.
“They would target me a lot, they would cook up stories – how I’m getting married… I’m training people to become lesbians,” Nabagesera said.
“People have lost housing, jobs, families,” she said. “One colleague was beaten in broad daylight after appearing in the newspapers.”
Nabagesera said in the last four years, the local media had played a “big role” in the intimidation and harassment of LGBTI people, after naming and shaming them.
In 2011 gay activist David Kato – a close friend of Nabagesera – was beaten to death with a hammer a few months after a tabloid paper published his picture under the headline ‘Hang Them’.
Christmas present
Nabagesera came up with the idea for Bombastic in 2013. When she asked for stories on Facebook, she was flooded with over 500 contributions. Crowd-funding paid for its printing.
An editorial team of eight Ugandans worked on the inaugural issue and foreign volunteers also pitched in helping to build a related website, www.kuchutimes.com, which Nabagesera said attracts so many visitors that it is “almost crashing every two days”.
“We got a lot of support from around the world,” said Nabagesera.
Bombastic was launched in December as MPs were vowing to introduce a new anti-gay bill as a “Christmas present”, after an earlier statute was struck down on a technicality in August.
“So we said let’s give them a Christmas present,” said Nabagesera.
A total of 15 000 copies of Bombastic have been printed and distributed by hand to some unlikely potential readers.
“We took lots of copies to Parliament, government offices, everywhere,” said Nabagesera.
She personally delivered copies, concealed inside brown paper envelopes, to the pigeonholes of MPs such as David Bahati, the architect of an early anti-gay law that sought the death penalty for homosexuals, to the office of the Speaker, Rebecca Kadaga, a staunch supporter of anti-gay legislation, and to the office of President Yoweri Museveni.
Nabagesera said she had not yet received any feedback from the politicians but had heard that, “the president’s wife refused even to open it.” First Lady Janet Museveni is an high-profile born-again Christian.
Big hit?
Churches, media houses, motorbike taxi riders and others across the country have also been handed the magazine, courtesy of 138 enthusiastic volunteers, some from the mainstream media.
“People are willing to be part of the project,” said Nabagesera.
Red Pepper, a notorious Ugandan tabloid which published a list of the country’s “top homos” a day after Museveni signed the first anti-gay bill into law nearly a year ago, was the first media house to be given copies.
“They refused to write about it, they were angry of course, because when you read my introduction I’m bashing the media,” said Nabagesera.
She insisted Bombastic had mostly been a “big hit”, adding that the magazine’s two telephone hotlines have been inundated with interest.
But some people have burnt issues after finding them in shops in eastern Uganda, while in the country’s west some distributors were threatened. Nabagesera herself was threatened with legal action after a copy was taken to a church.
Others told her they wished “a car could knock you down” while Uganda’s ethics minister Simon Lokodo warned she could face arrest for “promoting homosexuality”.
Nabagesera is undaunted. She hopes to continue publishing the magazine and to “stand up and fight for others who don’t have the support.”
“It is our wish, our hope, that if people read just one story it changes their attitude,” said Nabagesera.