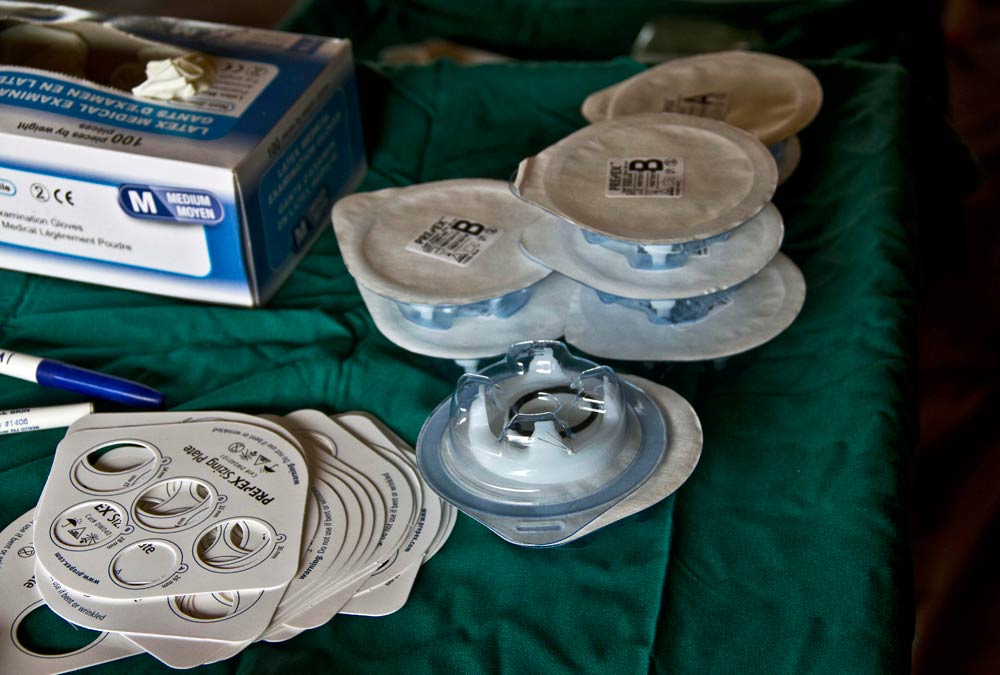
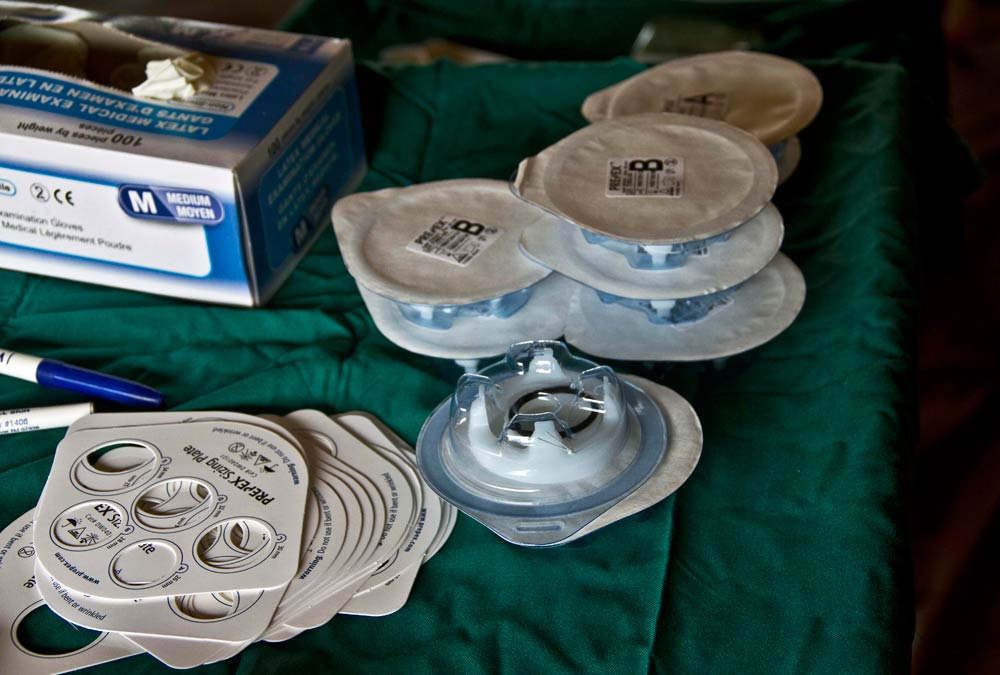
With trousers around his ankles, Justin Igalla awaits a tight rubber band for his foreskin, an innovative non-surgical technique rolling out in several African nations to encourage circumcision and cut HIV infection rates.
The simple device – two plastic rings and an elastic band – cuts off blood supply to the foreskin, which then shrivels and is removed with the band after a week.
“I felt nothing, not even a little discomfort,” Igalla said after a procedure taking just minutes, noting there was no blood – unlike traditional circumcision where the foreskin is sliced off by knife – thus reducing the risk of infection.
Igalla, a father of two, said he opted to have his foreskin taken off for “health reasons”.
Scientists have found that male circumcision can significantly reduce the chances of HIV infection because the foreskin has a higher concentration of HIV-receptors than the rest of the penis and is prone to tears during intercourse, providing HIV an entry point.
As well as Uganda, the device is being used in Botswana, Kenya, Mozambique, South Africa, Zambia, Zimbabwe and other sub-Saharan countries. All have been identified by the World Health Organisation (WHO) as “priority” states where the risk of acquiring HIV is high and male circumcision, and access to conventional surgical procedures, is low.
Uganda hopes the device, called PrePex, will convince adult men to be circumcised as part of the battle against Aids, now resurgent in the East African nation after years of decline, with as many as 80 000 people dying of the disease every year.
From a peak of 18% infected in 1992, Uganda’s “ABC” strategy – Abstinence, Be faithful, Condomise – helped slash rates to 6.4% in 2005.
But rates have crept back up, to 7.2% in 2012. As many as 1.8 million people in the country now live with HIV, and a million children have been orphaned after their parents died of Aids.
The makers of PrePex boast that a man “can resume work and almost all daily activities shortly after the procedure,” with the device “designed to be placed, worn, and removed with minimal disruption”, although they should abstain from sex for six weeks afterwards.
Doctor Barbara Nanteza, male circumcision project manager at Uganda’s Aids Control Programme, said that trials had shown that circumcision reduced risk of transmission from a woman to a man by as much as 60 percent.
Although some contest the validity of these studies, WHO and the United Nations Aids programme push circumcision as an additional prevention measure in high-prevalence countries where HIV transmission is predominantly heterosexual.
The WHO says there is “compelling evidence” circumcision reduces risk of heterosexually acquired HIV infection in men. The organisation has “prequalified” PrePex, meaning the device has been assessed and meets international standards for efficacy and safety.
And with health budgets already overstretched, the device offers a cheaper way to tackle the problem, Nanteza said.
“If circumcision can help reduce the cost, that could very good for the country,” she told AFP.
Uganda, long praised for its efforts in the fight against Aids, launched a general circumcision programme in 2010, when some 9 000 had the conventional treatment.
Since then 1.2 million men have been circumcised – or 13% of men over 15, including 800 000 last year alone, the health ministry said.
The introduction of the PrePex device is expected to boost numbers even further – but it’s still not enough, according to Nanteza.
Though the device greatly reduces the pain of traditional circumcision, she conceded the issue remained an awkward one for married men.
“It is difficult for them to explain to their wife that they want to get a circumcision to prevent HIV infection when they are supposed to be faithful to them,” Nanteza said.
Despite massive health awareness campaigns, problems remain.
James Brian, a counsellor with the Walter Reid Project, a US-based medical organisation supporting the programme, said it was essential to emphasise that while circumcision reduces the risk of infection, it does not prevent it.
“After circumcision someone should not think that they are immune against HIV,” Brian said, who works with patients to highlight the continuing need to practise safe sex.
Emmanuel Leroux-Nega for AFP