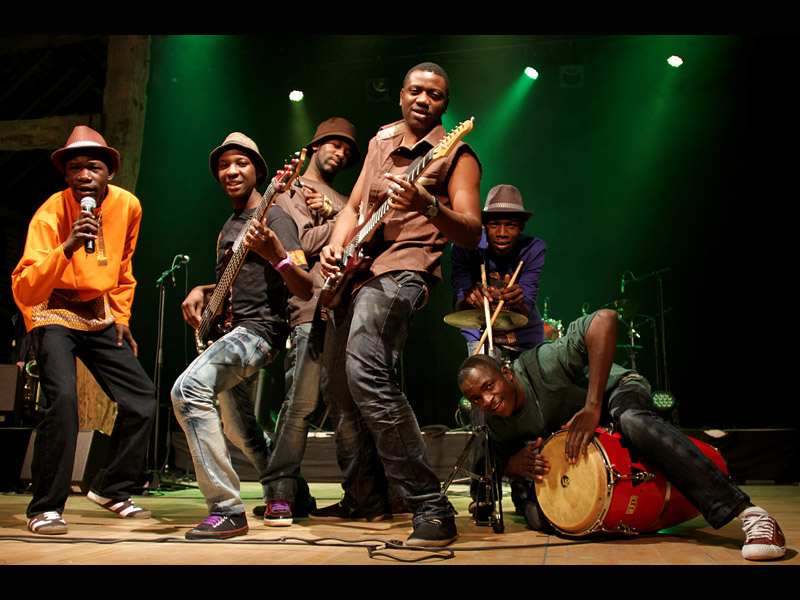
Abundance Mutori was just 14 when he began playing with the other members of Mokoomba. It was in 2002, when they were at school together at Mosi-Oa-Tunya High in Victoria Falls, Zimbabwe, and he remembers that their biggest problem was getting hold of instruments. “We didn’t have our own, and even at school when we had a music class we didn’t have any guitars or keyboards,” he says. “But my dad used to play in church and had a bass guitar at home, and he first showed me how to play. From then on, I was practising by myself or jamming with the guys.”
Now, in their mid-20s, Mokoomba are being feted as Africa’s most internationally successful young band after a rise that is as deserved as it has been remarkable. After all, they come from a country with an international musical profile that has sadly declined since the glory days of the 80s, largely because of Aids. Even in Zimbabwe they were initially considered outsiders. They sing in Tonga, a language that most Shona and Ndebele speakers can’t understand, and come from a tourist border town that’s a 12-hour drive from the capital, Harare.

The group are signed to a small Belgian label and were unknown in Britain until their second album, Rising Tide, was released there last August. But by the end of 2012, they were featuring in the annual “Best of” lists in publications from the Guardian to fRoots, and so it is no surprise that they should win Songlines magazine’s newcomer award, announced last week. This summer they will be playing at major festivals across Europe, including Womad in Britain.
They succeeded thanks to a mixture of determination, skill and luck. As teenagers, they got most of their experience with the help of a local bandleader, the late Alfred Mjimba, who was “the only guy with musical instruments in the area. You’d go round to see him, and try to play this or that, and if he liked what you did, he’d say: ‘There’s a gig, come and play with us.'” He was no major star, but he played in local hotels and small clubs – though it was initially impossible for Mutori to play in bars because he was the youngest member of the band, under-age, and his parents objected.
The would-be musicians lived in Chinotimba township, a “high-density” area that was first established in the pre-independence zone outside the smarter, affluent one reserved for white people and tourist hotels near the spectacular waterfall. As a border town, close to Zambia, Botswana and Namibia, Victoria Falls was a “melting pot”, according to Mokoomba’s young manager Marcus Gora. “When you were growing up there, you couldn’t escape different cultures, languages and musical influences. There was music from the local Tonga tradition, Congolese rumba and soukous, funk, pop from the Beatles, and even country. That’s what our parents played.”
The band reflects these different cultures. Mutori plays bass, and his bandmates include Trustworth Samende, an excellent guitarist, and the powerful, soulful singer Mathias Muzaza, who travelled widely in southern Africa as a boy with his Angolan and Zambian parents. The band played in restaurants, or busked for tourists, and developed their own distinctive style. “It’s Afro-fusion,” says Mutori. “A mixture of Tonga rhythms, soca, soucous and the other things we listened to growing up.”
Mokoomba broke out of Victoria Falls, and then Zimbabwe, with the help of the non-profit NGO Music Crossroads International, which organises workshops, festivals and competitions in Africa. The band took part in a local competition in 2007, and the following year were invited to the InterRegional festival and contest in Malawi – which they won. Their prize was to record a six-track album, which has not yet been released in Britain, and a European tour.
International success didn’t prove easy at first, but Mokoomba were at least getting noticed. In Malawi they had met Manou Gallo, the bass player and singer from Côte d’Ivoire, best known for her work with Zap Mama. She collaborated with the band at the HIFA Harare arts festival in 2010, then produced last year’s breakthrough Rising Tide. Enthusiastic reviews, and an impressive appearance on Later… with Jools Holland followed.
Now, as the band prepare for a lengthy summer tour, bolstered by their latest award, it seems that Zimbabwean music could enjoy an international renaissance. Of the country’s 1980s heroes, Oliver Mtukudzi is still in excellent form, while Thomas Mapfumo, who lives in the US, returns to Britain next month to play at the Field Day festival. But several of that glorious band the Bhundu Boys have died. “The momentum was lost because of Aids,” says Gora. “A whole generation was decimated, and they were the core of the music industry at the time.”
How do they feel about Robert Mugabe and the political upheavals in Zimbabwe? Gora is diplomatic. “As a band, we have made a conscious decision to build our career outside of politics until a time we are established enough to have an effective voice.”
Mokoomba may be leading the country’s international music campaign, but it has taken time for Harare audiences to appreciate their Tonga-language Afro-fusion, which has little in common with the fashion for the Congolese-influenced Sunguru music of local hero Alick Macheso. But that’s beginning to change, as Mokoomba spend more time living and performing in the capital. “Baaba Maal is appearing with us when we play [at] the Harare festival on May 5,” says Gora. “Mokoomba is becoming a big band.”