When an Internet message announcing a salt water solution for Ebola went viral in July, many Nigerians were quick to take heed. Twenty people were hospitalised and two died, reportedly from an excessive intake of salt.
Madam Franca was among those ready to believe in the power of salt water. “My niece, who happens to be a nurse, sent me an SMS that early morning, and I obeyed it,” Franca explained. “I had to do anything to stop Ebola from coming close to me. I bathed with salt water, morning and night for two good days, but I did not drink. I am hypertensive. I also sent all my family and close friends the SMS.”
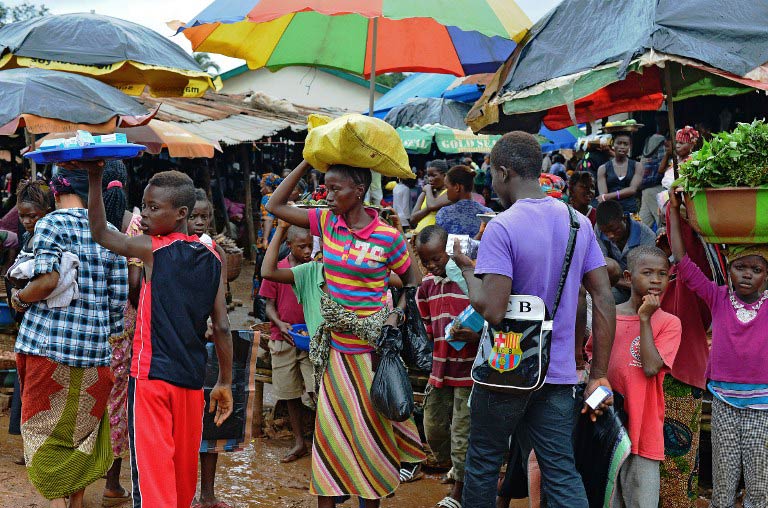
Nigerians watched with growing unease as the Ebola outbreak spread through Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia. Few believed the creaking health infrastructure or the government’s managerial skills would be able to survive such a test. So when Ebola-positive Liberian Patrick Sawyer stepped off a plane in Lagos airport on 20 July, collapsed and died, social media exploded.
But it was not just the salt water claims and bogus pastors promising salvation that made the running: government agencies and proactive individuals also took to the internet to quickly debunk the rumours and offer proper advice. The authorities also threatened to arrest anyone spreading falsehoods, starting with the salt water “cure”. There was, after all, a plan in place.
A mass audience for messages
At 67 million users, Nigeria reportedly has the eighth largest Internet population in the world. It also had close to 166 million mobile subscribers as ofJune. (The country’s population is 175 million.)
With so many Nigerians online, portals like ebolalert.org set up by volunteer doctors, and the public/private ebolafacts.com initiative, have become important channels to provide accurate information to help people stay safe. They complement telephone hotlines and more traditional public health approaches.
The UN Children’s Fund (Unicef) has also taken a role in the communications work on Ebola, using the SMS portal UReport. UReport Nigeria is a free SMS platform designed as a community-based two-way information exchange mechanism. According to Unicef communications specialist Geoffrey Njoku, over 57 000 people received more than 3.6 million SMSes containing key messages about Ebola and how to stay protected over a six-week period.
Comfort and confidence
For some who have used the service, like Dr Adoara Igonoh, an Ebola survivor, the advice given offered reassurance and quelled fears. “I began to think about my mother,” Igonoh recalled. “She was under surveillance along with my other family members. I was worried. She had touched my sweat. I couldn’t get the thought out of my mind. Hours later on Twitter I came across a tweet from the WHO [World Health Organisation] saying that the sweat of an Ebola patient cannot transmit it at the late stage [after the incubation period]. That settled it for me. It calmed the storms that were raging within me concerning my parents.”
Nigeria has won praise from the international community for its response to the outbreak. While Ebola continues to burn in Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea, in Nigeria it appears to have been contained with only 21 confirmed cases and eight deaths – with the last case reported on 8 September and tracing having proven effective.
“A key issue in the fight against Ebola after the provision of the necessary human and technical infrastructure is information management,” said Tochuwu Akunyii, an online writer on public policy and international development. “In information management, the dissemination of accurate information is crucial; social media can be vital in this process.” Akunyii pays particular tribute to Nigerian youth and its use of forums and platforms like Twitter and Facebook.
Social media complemented traditional media
Nigerians who do not have access to the Internet and mobile phones have not been left out of the Ebola campaign. Traditional mediums like radio, flyers, posters, village meetings and announcements by town criers are all being used. Priority is given to local languages.
Comparing the traditional methods of campaigning to social media and SMS campaigns, Nwokedi Moses, better known as Big MO, a vernacular language broadcaster with Wazobia FM, said the two approaches worked well together. “The social media Ebola campaign was massive, but it complemented the traditional media. This is due to social media’s limited reach within rural areas.”
Local authorities have also taken the initiative. The Lagos State and Rivers State governments – the only two states where Ebola emerged – incorporated traditional awareness-raising campaigns like road shows, radio and TV jingles, distributing flyers, and educating the public on basic hygiene. Since Ebola first emerged, there has been a roaring trade in hand sanitizers and a corresponding collapse in the “bush meat” market.
As Nigeria gradually returns to normal, signalled by the slightly hesitant reopening of schools on 22 September, health campaigners are moving to tackle the new challenge of ending the stigmatisation of those who have recovered from Ebola – backed by a government warning threatening action against those that discriminate.
Lagos State Governor Babatunde Fashola recently met survivors to confirm that an Ebola-free certificate means what it says. Health Minister Onyebuchi Chukwu has declared survivors the “safest people to be around”, given their new immunity to the virus.