Among the washer women, carpenters, busy waiters and squabbling children sweltering under the midday sun on this dusty Dakar street, an internet revolution is taking place in the world’s first tablet café.
Next to the workshops, meat stores and barbershops on what could be any bustling street in sub-Saharan Africa, a grey concrete building stands out with a garish sign advertising the Tablette Café.
“This is the first tablet café in the world, a café that works with tablets,” said Tidiane Deme, the head of Google in French-speaking Africa.
The concept, introduced by the internet search giant, is a simple twist on the traditional cyber cafés which have been springing up across Africa as the internet boom takes hold, ditching PCs for tablet computers.
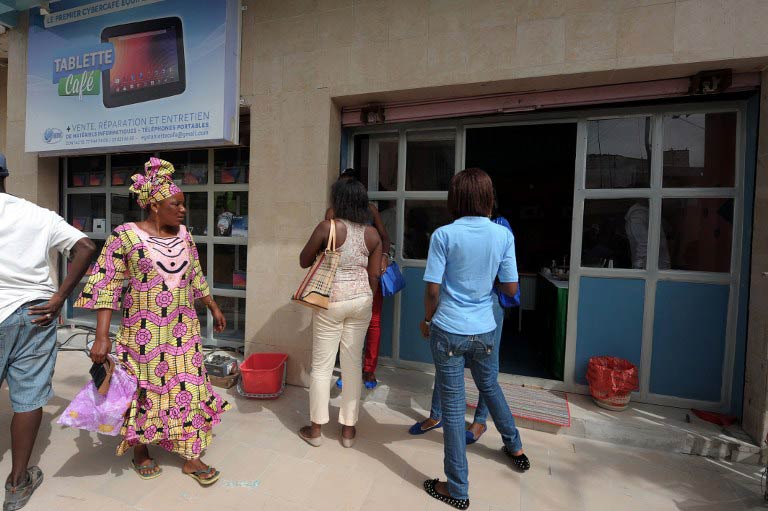

When Medoune Seck (33) opened his Equinoxe cyber café six years ago, he quickly discovered that frequent power cuts and exorbitant electricity bills were a major headache for him and his customers.
Then along comes Google which offered funding last year to turn one cyber café in Africa into a pilot tablet café. Seck applied and his café was picked as their guinea pig.
While tablets have taken advanced industrialised countries by storm and pushed cyber cafés further to the margins, in the developing world they could lead to their renaissance.
Tablet cafés could take hold in Africa because most people cannot afford to buy the devices, and tablets use batteries and mobile data connections which make them not vulnerable to power cuts.
The Equinoxe now sports 15 tablets and has installed cabins for private video chats, while a corner of the café is given over to a shop selling various items of electronic equipment.
Three PCs remain enthroned on boxes near a wall, but they do not generate much interest among clients, who recline on the café’s bright orange and blue sofas, jabbing at their touch screens.
Seck says his tablets cost more than PCs but they save on power bills as they consume 25 times less electricity.
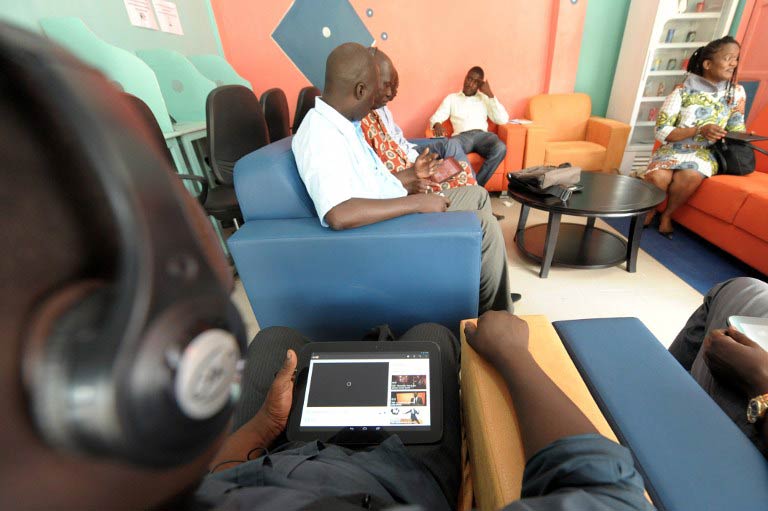

He believes they can help revive cyber cafés which, according to Google, are in something of a slump precisely because of the high cost of electricity and frequent power failures cutting into business.
“Tablet computers will revolutionise Africa, and Senegal,” said Seck.
The simplicity of using the touchscreen devices could help bring computing to scores of new people.
An elderly grandmother in a billowing bubu robe, headscarf and sash from the house opposite the café was among the first through the doors to “bless” her neighbour’s business, and she left amused after being given an introduction to using a tablet.
Mamadou Camara, a 16-year-old Facebook and Skype user, enthused about the improved computing experience of tablets.
He complained about “cyber café PCs which are very slow and exhaust your credit”.
Upon arrival, customers hand over an ID card and pay in advance for a set connection time before they are given a tablet.
When they leave the device is reset, wiping out any data from their session, and it is ready for the next customer.
The Tablette Café charges the same price as its predecessor did for PCs: 300 CFA francs (80 US cents) per hour.
“Our hope is that cyber cafés attract new customers interested in a more simple and interactive way of going online, and make significant savings on their number one operating expense: electricity,” Alex Grouet, Google’s business development manager in Francophone Africa, said in a blog post.
Café owners should be able to invest the savings on electricity costs into improving their connection speeds, he suggested, thereby boosting their clients’ experience.
“We look forward to finding out as the project unfolds, and hope that people living in Dakar will stop by to try out something new.”
Coumba Sylla for AFP.