Kenya has given the United Nations three months to remove a camp housing more than half a million Somali refugees, as part of a get-tough response to the killing of 148 people by Somali gunmen at a Kenyan university.
Kenya has in the past accused Islamist militants of hiding out in Dadaab camp which it now wants the UN refugee agency UNHCR to move across the border to inside Somalia.
“We have asked the UNHCR to relocate the refugees in three months, failure to which we shall relocate them ourselves,” Deputy President William Ruto said in a statement on Saturday.
“The way America changed after 9/11 is the way Kenya will change after Garissa,” he said, referring to the university that was attacked on April 2.
Emmanuel Nyabera, spokesperson for the UNHCR in Kenya, said they were yet to receive formal communication from the government on the relocation of Dadaab and could not comment.
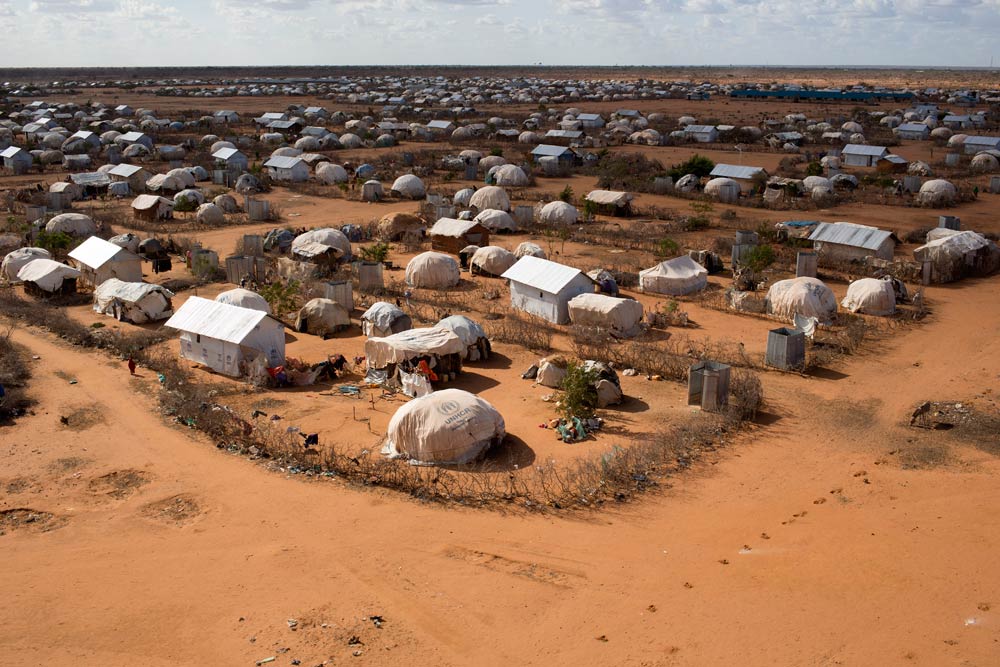
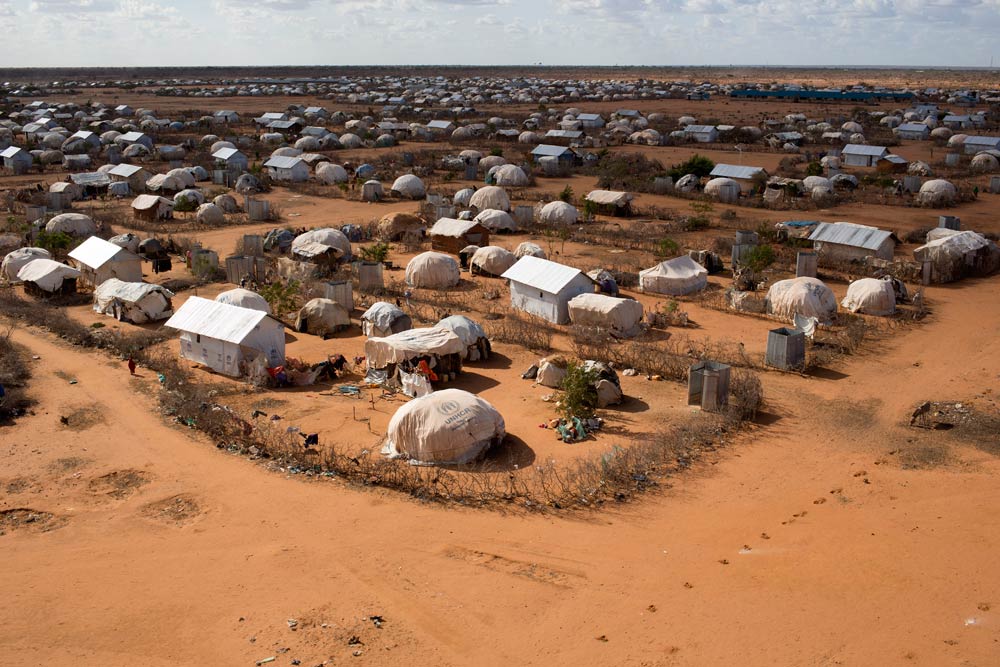
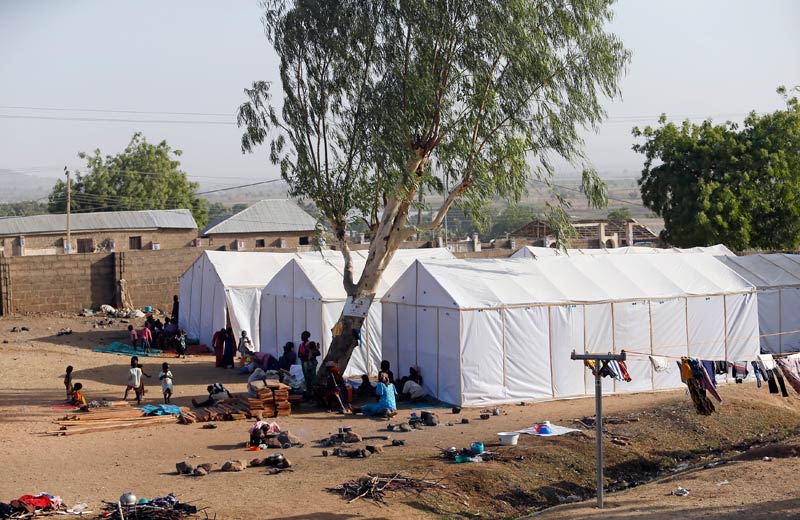
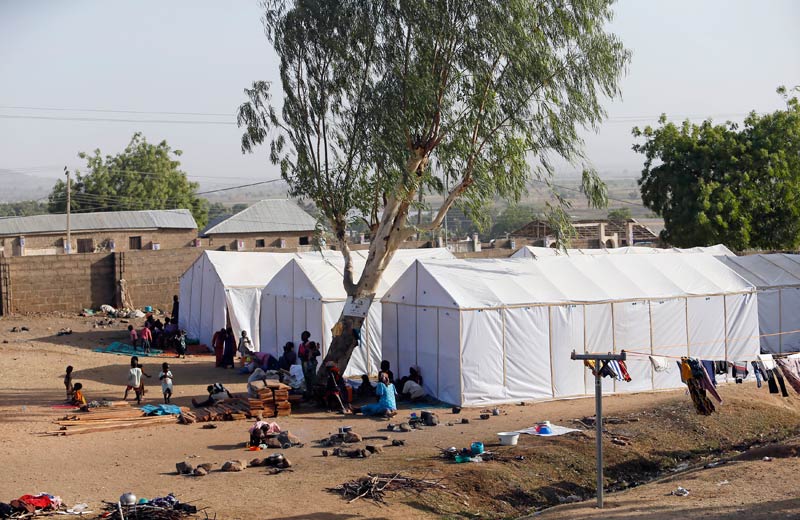
The complex of camps hosts more than 600 000 Somali refugees, according to Ruto, in a remote, dry corner in northeast Kenya, about an hour’s drive from Garissa town.
The camp was first established in 1991 when civil war broke out in neighbouring Somalia, and over subsequent years has received waves of refugees fleeing conflict and drought.
The United Nations puts the number of registered refugees in the chronically overcrowded settlements of permanent structures, mud shanties and tents, at around 335 000. The camp houses schools, clinics and community centres.
Macharia Munene, professor of international relations at USIU-Africa, said the logistics of moving hundreds of thousands of refugees across the border would be “a tall order”.
But he said there were now safe areas within Somalia from where Islamist al Shabab militants had been chased out by African Union forces in recent years.
“Kenya is in an emergency situation… Each country has an obligation to look after its people first,” he told Reuters.
‘We must secure this country at all costs’
Funerals of the students killed in the campus attack were taking place across the country. Pictures of their grieving families dominated the media, reminding Kenyans of the attack.
Ruto said Kenya had started building a 700-km wall along the entire length of the border with Somalia to keep out members of al Shabab.
“We must secure this country at whatever cost, even if we lose business with Somalia, so be it,” he said.
On Tuesday, Kenya closed 13 informal money remittance firms, hawalas, to cut off funding to suspected radicals. Ruto said any business that collaborated with al Shabab would be shut down.
Al Shabab has killed more than 400 people on Kenyan soil in the last two years, including 67 during a siege at Nairobi’s Westgate mall in 2013, damaging tourism and inward investment.
On Monday, the Kenyan air force launched air strikes against al Shabab targets in Somalia, a country where it has been militarily engaged against the Islamists for several years.